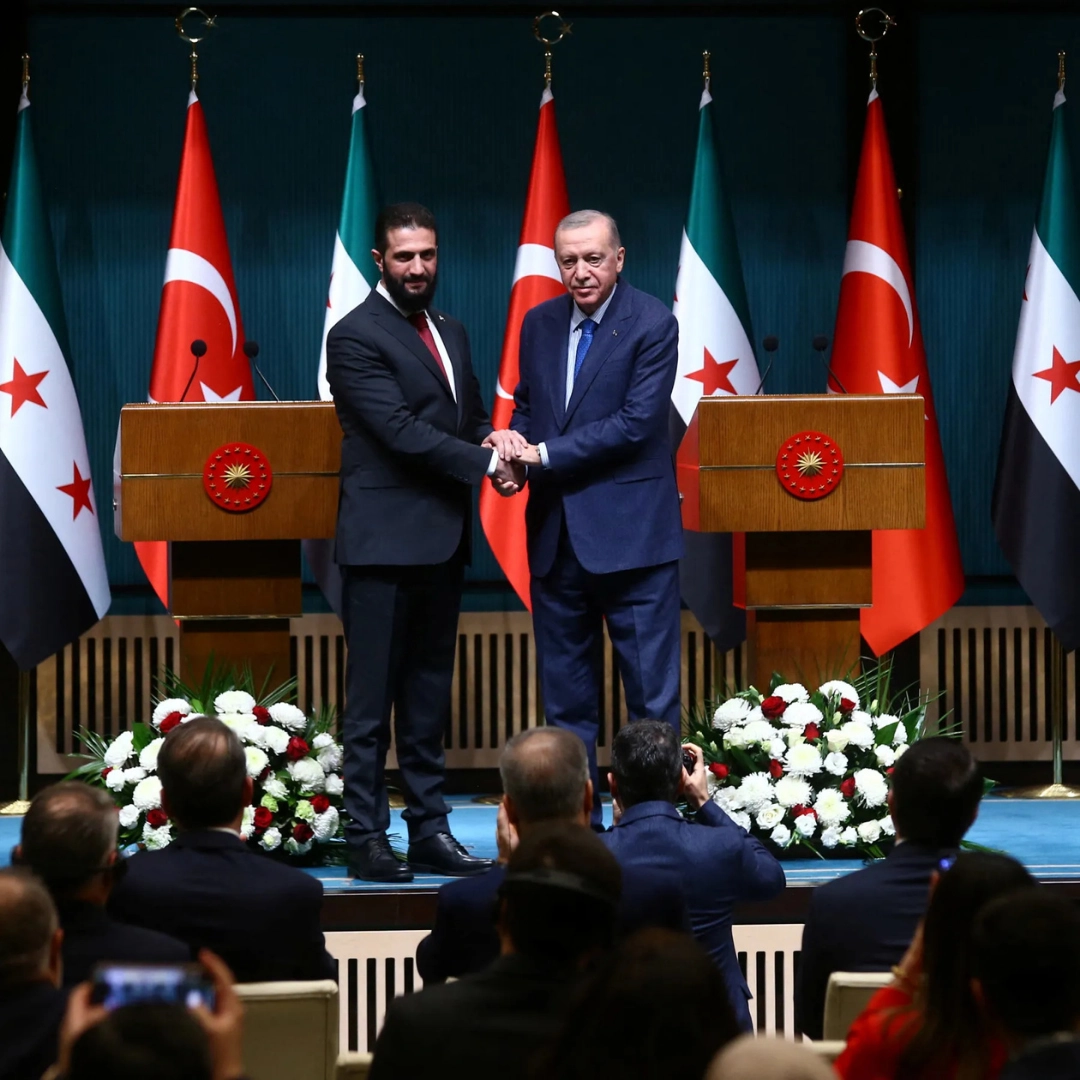
Turkey's Strategic Role as Security Guarantor for Kurds in Northern Syria
What does it mean for a nation to declare itself the security guarantor for an ethnic group in a neighboring country? Why would Turkey position itself as the protector of Kurdish populations in Syria, and how does this complex geopolitical stance impact regional stability? These questions lie at the heart of President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan's recent declaration that "Türkiye is the guarantor of Kurds' security in Syria" – a statement that carries profound implications for Middle Eastern politics, international relations, and the ongoing Syrian conflict.
Historical Context: The Turkish-Kurdish Dynamic
The relationship between Turkey and Kurdish populations has been historically complex, marked by periods of tension, conflict, and attempted reconciliation. For decades, Turkey has engaged in counter-insurgency operations against the Kurdistan Workers' Party (PKK), designated as a terrorist organization by Turkey, the United States, and the European Union. This historical backdrop makes Turkey's positioning as a security guarantor for Syrian Kurds particularly significant.
The Syrian civil war, beginning in 2011, created a power vacuum in northern Syria that allowed Kurdish groups, particularly the People's Protection Units (YPG), to establish autonomous administrations. Turkey views the YPG as an extension of the PKK, creating a paradoxical situation where Turkey simultaneously opposes certain Kurdish militant groups while claiming to protect Kurdish civilians. This dual approach reflects the nuanced reality of modern geopolitics, where national security interests and humanitarian concerns often intersect in complex ways.
Real-world example: Turkey's Operation Olive Branch in 2018 demonstrated this complex approach. While targeting YPG positions in Afrin, Turkey simultaneously established local governance structures and provided humanitarian aid to Kurdish civilians, illustrating the dual nature of its policy – combating what it perceives as terrorist elements while supporting civilian populations.
Turkey's Security Doctrine and Cross-Border Operations
Turkey's security doctrine has evolved significantly in response to regional threats, particularly following the rise of ISIS and the expansion of Kurdish-controlled territories along its southern border. The country has conducted several major military operations in northern Syria, including Euphrates Shield (2016), Olive Branch (2018), Peace Spring (2019), and Spring Shield (2020). These operations serve multiple purposes: eliminating terrorist threats, creating buffer zones, and facilitating the return of Syrian refugees.
The practical application of Turkey's security guarantee involves establishing controlled zones where Turkish military presence deters both Kurdish militant groups and other extremist organizations. In these areas, Turkey has invested in infrastructure, healthcare, and education, attempting to create models of stability that contrast with both regime-controlled areas and Kurdish-administered regions. This approach represents a comprehensive security strategy that combines military, political, and humanitarian elements.
For instance, in the areas controlled through Operation Peace Spring, Turkey has built residential complexes, hospitals, and schools while maintaining military security. This dual approach aims to address both immediate security concerns and long-term stability through development, representing a modern counterinsurgency strategy that recognizes the importance of winning civilian support.
Regional and International Reactions
Turkey's positioning as security guarantor has elicited mixed reactions from regional and international actors. The United States, which partnered with YPG-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) in the fight against ISIS, finds itself in a delicate position, balancing its alliance with Turkey against its tactical cooperation with Kurdish forces. Russia, another key player in Syria, has engaged in complex diplomacy, sometimes facilitating agreements between Turkey and Kurdish groups while advancing its own strategic interests.
Regional powers like Iran have viewed Turkey's expanded role with suspicion, concerned about increased Turkish influence in areas bordering their sphere of influence. Meanwhile, European nations have expressed concerns about humanitarian aspects while recognizing Turkey's legitimate security interests. This complex web of international relations demonstrates how Turkey's declaration impacts not just bilateral relations but the entire geopolitical landscape of the Middle East.
A practical example of these complex dynamics emerged during the October 2019 situation when American and Turkish forces found themselves in close proximity during Turkey's Operation Peace Spring, requiring delicate diplomatic and military coordination to prevent accidental clashes between NATO allies.
Humanitarian Dimensions and Refugee Considerations
Turkey's role as security guarantor extends beyond military concerns to encompass significant humanitarian aspects. Hosting over 3.6 million Syrian refugees – the largest refugee population in the world – Turkey has a vested interest in creating stable conditions in northern Syria that would enable voluntary returns. This humanitarian dimension adds complexity to Turkey's security calculations, intertwining domestic political pressures with international obligations.
The practical application of this humanitarian-security nexus is visible in Turkey's establishment of so-called "safe zones" along the border. These areas are intended to provide security for both local populations and returning refugees, addressing both Turkey's security concerns and its refugee management challenges. However, humanitarian organizations have raised concerns about the voluntary nature of returns and the conditions in these zones, highlighting the tension between security objectives and humanitarian principles.
For example, in areas under Turkish control, authorities have worked with international organizations to provide services while maintaining security control. This balancing act represents the practical challenge of implementing Turkey's declared role as security guarantor while meeting international humanitarian standards.
Legal and Sovereignty Implications
Turkey's positioning as security guarantor raises significant questions about state sovereignty and international law. While Turkey justifies its actions under the right of self-defense against terrorist threats, critics argue that its cross-border operations violate Syrian sovereignty. This tension between security needs and respect for territorial integrity represents a broader challenge in contemporary international relations, where non-state actors and transnational threats complicate traditional notions of sovereignty.
The legal framework for Turkey's actions references multiple justifications, including UN Security Council resolutions on combating terrorism, bilateral agreements with previous Syrian governments, and the evolving concept of responsibility to protect. However, the lack of explicit UN authorization for specific operations creates legal ambiguities that different actors interpret according to their political interests.
A real-world application of these legal complexities emerged during Turkey's military operations, where different international actors invoked different legal frameworks to either support or condemn Turkey's actions, demonstrating how international law remains contested terrain in geopolitical conflicts.
Future Implications and Regional Stability
Turkey's declared role as security guarantor for Syrian Kurds will likely have lasting implications for regional stability, Kurdish aspirations for autonomy, and the future resolution of the Syrian conflict. This positioning establishes Turkey as an indispensable actor in any political settlement in Syria, ensuring that Turkish security concerns will be central to future arrangements in northern Syria.
The practical application of this guarantor role may involve Turkey influencing governance structures in Kurdish-majority areas, potentially supporting alternative Kurdish political movements that align with Turkish interests rather than the YPG-dominated administration. This could reshape the political landscape of northern Syria, creating new dynamics between different Kurdish factions and between Kurds and other ethnic groups.
Looking forward, Turkey's stance may also affect broader regional relationships, particularly with Russia and the United States, as all parties negotiate the future of Syria. The success or failure of Turkey's approach could influence how regional powers address similar ethno-political conflicts elsewhere, potentially establishing precedents for cross-border security guarantees in contested regions.
For instance, if Turkey's model of establishing secure zones with development projects proves successful in creating stability, it might be referenced in other conflict zones where security concerns intersect with humanitarian challenges and refugee returns.